TestNG annotations are defined before methods in the Test class to control the next batch of code/method to be executed.
If in case any of the annotations are NOT defined in front of a test method, the compiler just ignores and executes it as a part of the Test class.
We've them defined in three ways :
| Pre-Conditions | @BeforeSuite @BeforeTest @BeforeClass @BeforeMethod |
| Test | @Test |
| Post-Conditions | @AfterSuite @AfterTest @AfterClass @AfterMethod |
| Others | @Parameters @DataProvider @Listeners @Factory |
Let’s check on the usage :
| Annotation | Explanation |
| @BeforeSuite | Executes once Before the execution the tests in the suite are executed. |
| @AfterSuite | Executes once After the execution of all the tests in a particular suite is completed. |
| @BeforeTest | Executes Before the first @Test annotated method. This can be executed multiple times before the test case. |
| @AfterTest | Executes After the first @Test annotated method. This can be executed multiple times before the test case. |
| @BeforeClass | Executes Before first @Test method execution. This is done only once throughout the test case. |
| @AfterClass | Executes After first @Test method execution. This is done only once throughout the test case. |
| @BeforeMethod | Executes Before every @Test method execution. |
| @AfterMethod | Executes After every @Test method execution. |
| @BeforeGroups | Executes Before the first test run of a specific particular group. |
| @AfterGroups | Executes After all the test methods of a particular group. |
| @Test | It is a method that is part of the Test. |
| @Parameters | Used to pass parameters to the Test method. |
| @Factory | Used to represent a method as a Factory that returns Object[] for further usage in test classes. |
| @DataProvider | Acts as a data supplier for the @Test method, the respective annotated method must always return Object[][] and the name of the dataProvider during the definition must match with the one annotated in the @Test method. |
| @Listeners | Used for logging and reporting. |
Code Example :
import org.testng.annotations.*;
public class TestNGAnnotations {
@BeforeTest
public void beforeTest() {
System.out.println("-- Before Test -- ");
}
@AfterTest
public void afterTest() {
System.out.println("-- After Test --");
}
@BeforeMethod
public void beforeMethod() {
System.out.println("-- Before Method --");
}
@AfterMethod
public void afterMethod() {
System.out.println("-- After Method --");
}
@BeforeClass
public void beforeClass() {
System.out.println("-- Before Class --");
}
@AfterClass
public void afterClass() {
System.out.println("-- After Class --");
}
@BeforeSuite
public void beforeSuite() {
System.out.println("This will execute Before Suite");
}
@AfterSuite
public void afterSuite() {
System.out.println("This will execute After Suite");
}
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("Test method");
}
}
Output :
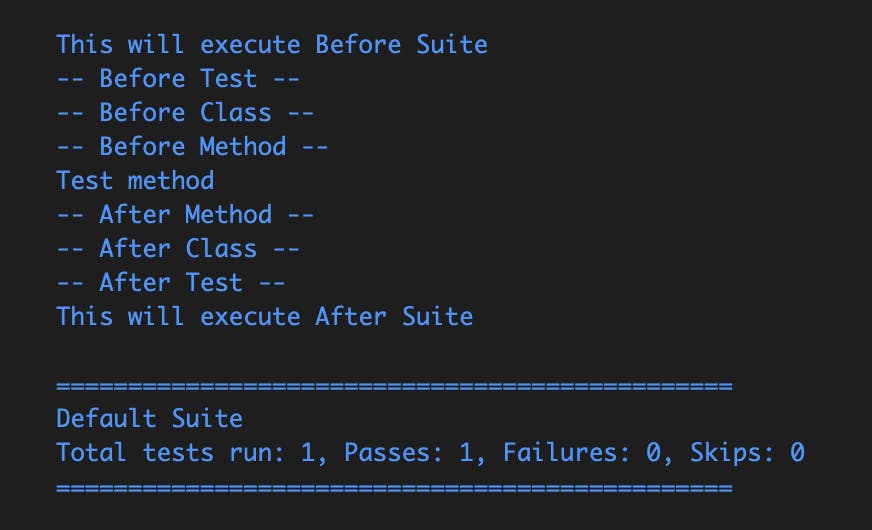
Sequence of Execution
I hope this TestNG tutorial, helped you to learn in detail about the TestNG annotations.
If you have any questions related to the article, let me know.
I look forward to your replies. Happy testing! :)


